Handlebars
Handlebars is a templating engine that supports dynamic content generation by inserting variables, and logic into content. You can read more about Handlebars on their website.
In Intellectible, Handlebars syntax is used for templating throughout the workflow editor. Most notably in the Text node. You can use Handlebars syntax to template data into the Text node, this might be text from a document, search result, or a form input. This creates a powerful system for combining your retrieved and generated data into text content as well as a way to access variables and data from other nodes.
Examples
Text nodes
In both the Text and the Plain Text nodes you can use Handlebars syntax to template data into the text content.
Including a variable
You include a variable in your text content by wrapping the variable name in double curly braces:
In the Text node, you will see that if you include a variable in the text content, a new input port will appear on the node.
If you have saved a variable in the workflow, you can also use it in the text content, without having to connect it to input port.
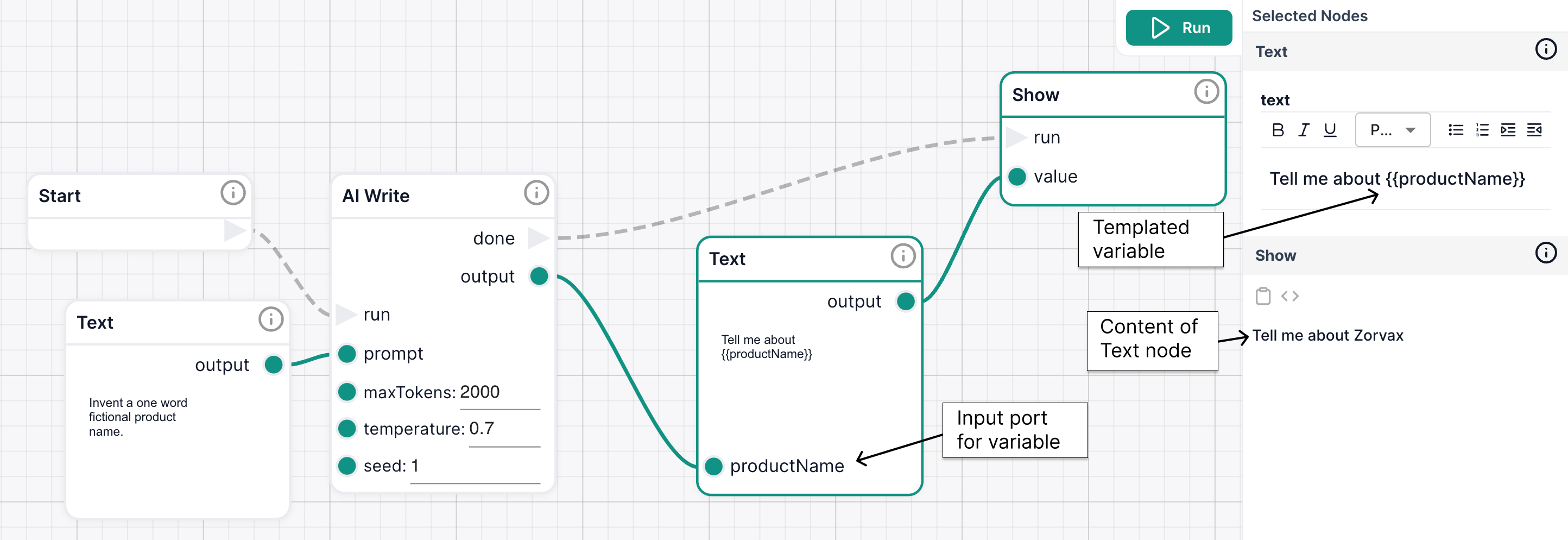
The example below contains a simple workflow, that generates a fictional product name and templates it into a prompt.
Notice how when we visualize the text in the Show node, we can see the value of productName.
Using the each helper with lists
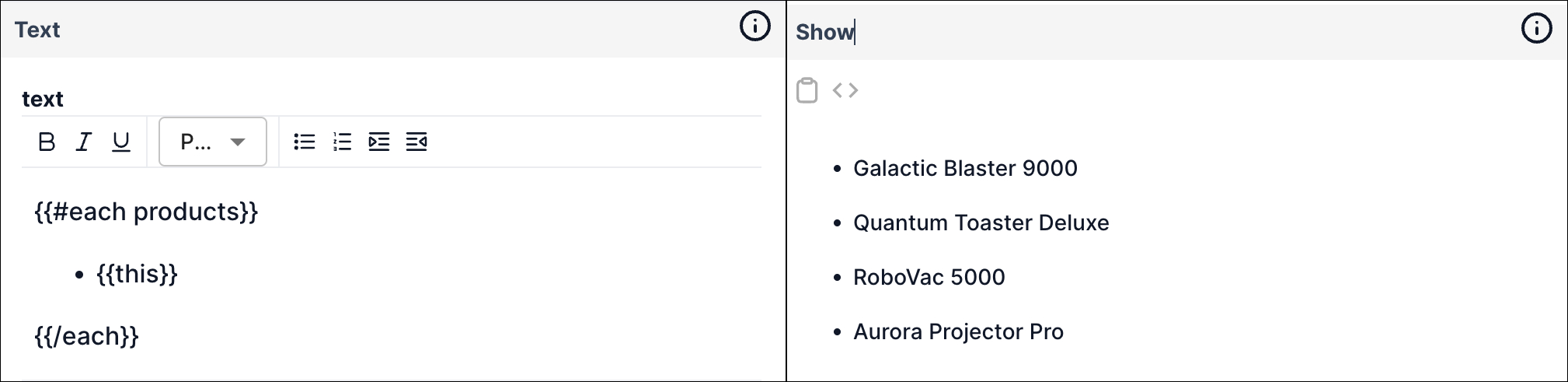
You can also make use of the Handlebars each helper to loop over a list of items and template them into the text content.
For example, we may have a list of product names that we want to template into our Text node. In the example below, an input port for the products variable will appear on the node and it will expect a list.
Accessing dictionary properties
If you have a list of dictionaries you can access the properties using dot notation. For example when you choose Dictionary output on the ReadCSV node, you will get a list of dictionaries. You can access the properties of the dictionary like this:
or if the properties (column headers) contain spaces, use square brackets to access them:
By default, Handlebars will escape HTML characters in the text content. If you want to disable this behaviour, you can use the triple curly braces syntax:
This will output the raw HTML without escaping it. If you are noticing weird encoding issues, such as ampersands being replaced with &
try this syntax.
Variable nodes
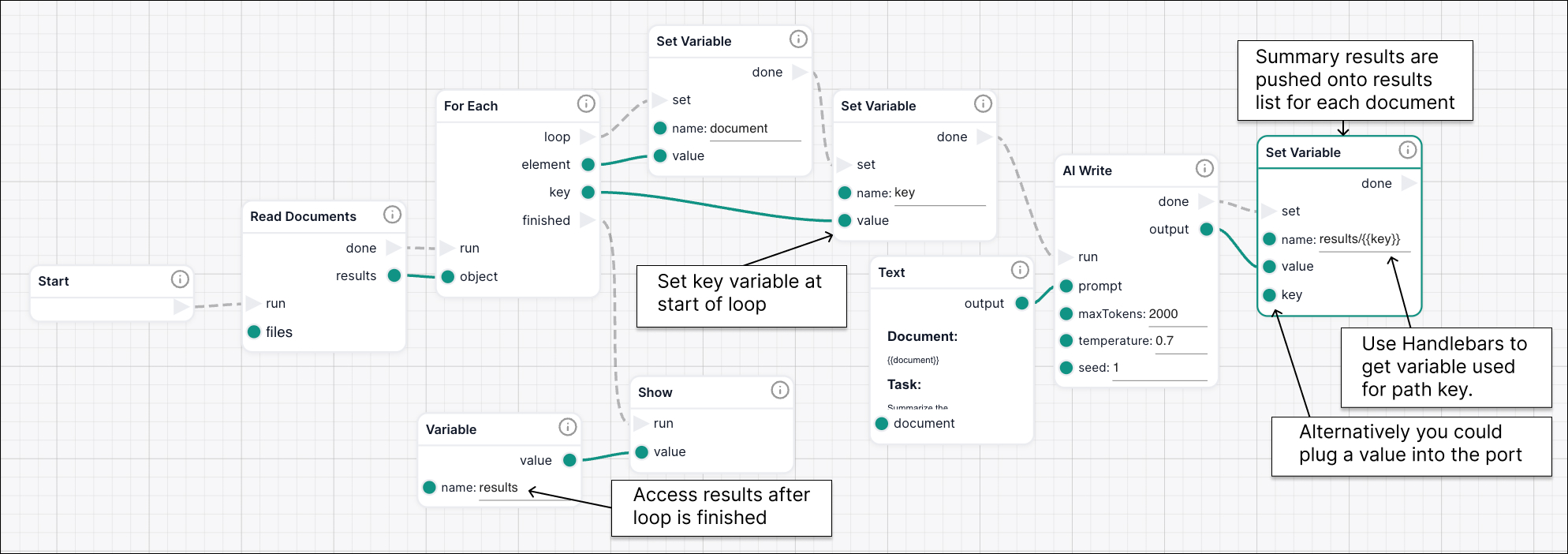
Handlebars templating can also be used within the variable nodes, Set Variable, Variable, and Get Value. For example, you may want to set a current variable to a path of another variable. This is a common behaviour when looping over a list with the For Each node and adding the results to a new list.
In the example below you can see a workflow that reads in a list of documents from your library,
loops over each document with For Each and summmarizes it with AI Write, the result is then added to a list variable called results.
The key from the For Each node, in this case referring to the Read Documents list index, is set to a variable called key.
After the AI Write operation is complete we use Set Variable to add the AI Write output to the results, using key as the list index.
The handlebars syntax allows us to grab that variable and add it to the path of results.
An input port also appears on the left of the node that can also be used if there is no saved variable with that name.
See For Each for more information about how the For Each node works.